DHCPv6 does not use the "Broadcast" but the "Multicast".[1][2] Multicast is a technique used for a device to send a single packet to multiple destinations simultaneously. An IPv6 multicast address defines a group of devices known as a multicast group. It is the IPv4 equivalent of 224.0.0.0/4. Unlike the IPv4, there is no broadcast address in IPv6.
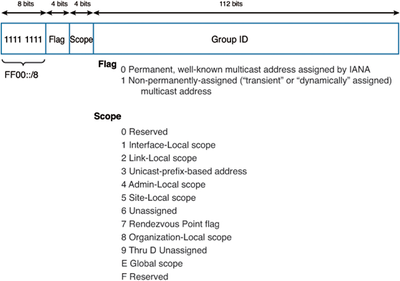
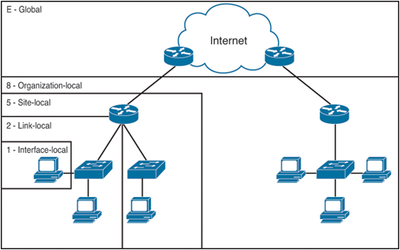
IPv6 multicast address have the prefix FF00::/8. The first 8 bits are 1(FF), followed by a 4 bit Flag and a 4-bit Scope. The next 112 bits represent the Group ID.
The Flag field indicates the type of multicast address, The two types of multicast addresses are.
- Permanent(0): These are well-known multicast addresses assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
- Nonpermanent(1): There are "transient" or "dynamically" assigned multicast addresses.
RFC 2375[3], IPv6 Multicast Address Assignments, defines the initial assignment of IPv6 multicast addresses that have permanently assigned Global IDs. In other words, these are reserved multicast addresses for predefined group or devices.
Some Well-Known Multicast Addresses[4] are
| Address | Scope | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ff01::1: | 1 | All-nodes |
| ff01::2: | 1 | All-routers |
| ff02::1: | 2 | All-nodes |
| ff02::1:ff00:1: | 2 | Solicited node multicast address for router's global unicast address |
| ff02::1:ffE9:d480: | 2 | Solicited node multicast adddress for router's link-local address |
| ff02::2: | 2 | All-routers |
| ff02::5: | 2 | OSPF-routers |
| ff02::1:2 | 2 | All-DHCP-Relay-agents-and-servers |
| ff05::2: | 5 | All-routers |
| ff05::1:3 | 5 | All-DHCP-servers |