Systems
We called the imRAD device as "System". If you configure an IP address in a system, the information of the system is automatically saving in a few seconds and this menu shows all the saved systems.
Device
This page lists all imRAD N1 systems.
System Information
This page shows the details of a system.(The smgr and the wd service in each device saves the information every 10 minutes.) The smgr service reads and saves the following information.
- General system information(i.e. version, serial number, uptime, model, and so on)
- Disk(storage), Memory(RAM), and CPU Load.
The wd service reads and saves
- The status, version, and information of operating service
If you click the "greater than" icon(>) in front of the IP address on each list, you can display more system information.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| IP Address | It is the IP address of the system. If the system has multiple same version addresses, it displays only one address of them. |
| Name | It is the hostname or system name of the system. You can change it via the CLI. |
| Serial number | It is the serial number of the system. |
| Update Date | It is the last datetime the information is saved. If this time is not updating for the "Idle detection timeout for system activity", we notice the system as "System Idle". |
| Status | It shows the status of disk[1] utilization and services. If each disk utilization exceeds the "Warning threshold for Disk utilization rate", it shows a "Notice" icon. If each disk utilization exceeds the "Critical threshold for Disk utilization rate", it shows a "Critical" icon. In the rest of the cases, it shows a "Normal" icon. If an enabled service is not running, it shows a "Notice" icon. If you click the trash icon, It will delete the system information. If the deleted system is still running, the information will be saved again. |
| Uptime | It indicates how long the system has been running. |
| Description | It is the description of the operating system. |
| Version | It is the current imRAD package version. If you click the icon( |
| RAM Disk(OS) Disk(Data)[1] |
It is the availability of each resource. |
| CPU Load | It shows the CPU load averages over the last 1, 5, and 15 minutes. |
| Current Failover Mode | It indicates the current mode of System Failover. If the System Failover is not configured, It shows "Not Configured". If the System Failover is configured, it shows either "active" or "passive". The Datetime beside the mode(i.e. active or passive) is the time of the mode was applied. |
| Database Replication | If the System Failover is not configured, this item does not display. If the System Failover is configured, it show "Not Configured", "Master", or "Slave".
The "Not Configured" means that a system is not configured to replicate database. This case is not a normal condition. Therefore, you need to configure the System Failover again. The circle icon in from of the replication mode(i.e. "Master" or "Slave") indicates the status of the database replication. |
Services
It shows all services(daemons) in a system. The status can be either "Active" or "Inactive". The "Active" indicates the service is running and the "Inactive" indicates the service has been stopped. The "Update Date" is the last time the service was checked. The "Uptime" is the time of the service was started.
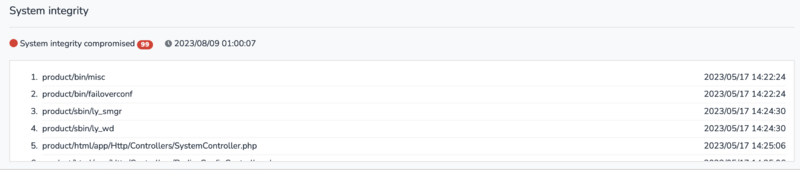
System Integrity
This system performs a system integrity check once a day (every day at 1 AM) and displays the integrity check results. If any changes or damage occur in any of the operating files, an integrity error may be displayed, and in such cases, a system update is required. To immediately check system integrity, click the icon(![]() ) on the system status, and within a few seconds, the check results will be displayed again. The image below shows the screen displayed when there are no compromised files and there are more than one compromised files each other.
) on the system status, and within a few seconds, the check results will be displayed again. The image below shows the screen displayed when there are no compromised files and there are more than one compromised files each other.

Database
Main Database Variables
It shows some key information of the database global variables. If you click the "plus" icon beside the title(i.e. "Main Database Variables"), you can see the information.
You may open an issue[3] when you think the database may have some problems. In such a case, you must include this information.
Database Replication Status
It shows the primary(master) and secondary(salve) status of MySQL Replication. It only appears in the environment of the failover configured.
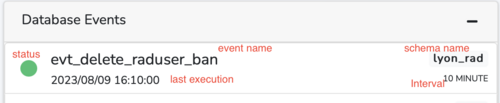
Main Database Events
Events are named database objects containing SQL statements that are to be executed at a later stage, either once off, or at regular intervals.[4] Several events are running in the database of the imRAD system. If you click the "plus" icon beside the title(i.e. "Main Database Events"), it shows all events and their status.
The icon in front of a event name indicates the event status. The green color means the event is ok, the yellow color indicates the event is disabled and the gray color notes the event is in the SLAVESIDE_DISABLED.[5]
If one of the events is not ok, you must enable them. If you click the icon red or gray-colored, you can enable an event.
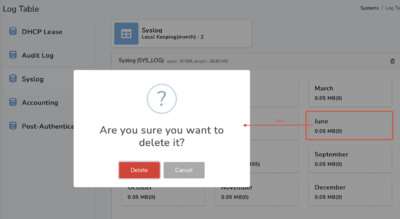
Log Table
It displays the size of operational log stored in local database. All data is managed on a monthly basis, and if the system's storage space is insufficient, you can click on a specific month of a specific log, as shown in the following image and you can delete all log for a specific month.
Syslog
The logexp service reads the Syslog[6] in its system and saves them into the imRAD database. It shows such Syslog.
However, The logexp service reads logs only whose level is greater than the "Informational".
In other words, If you want to see logs whose level is "Informational", you can see it from the CLI.
If you click the icon in front of each row, it shows the details of each log.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 The imRAD disk consists of two partitions. One is for the operating systems, another is for data.
- ↑ https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/replication-administration-status.html
- ↑ https://issue.basein.net
- ↑ https://mariadb.com/kb/en/events/
- ↑ https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/show-events.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syslog