| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
| − | You can | + | === Dedicated Log Server === |
| + | You can operate a dedicated Log Server that can store more logs than the imRAD local database. If you configure it, the management interface reads logs from the dedicated Log Server and displays them. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
==== Installing database server ==== | ==== Installing database server ==== | ||
| − | + | Install MariaDB 10.0 or higher Database server on your server. MySQL 5.7 or higher is also available. It doesn't matter which operating systems of the database server. | |
| − | + | ==== Downloading an SQL file ==== | |
| + | Open the "Dedicated Log server" page that is located in the "Environment" menu of the management interface. And then, download an SQL file by clicking the <i class="fas fa-download"></i> icon on the top right of the "Target log" table and save it on your computer. | ||
| − | + | ==== Importing an SQL file ==== | |
| + | Copy the SQL file into your log server(i.e. Dedicated Log server) and import it into your database by using the <code>mysql</code> command.<br> | ||
If you import the SQL file, it will create a user account, databases, and tables. The default user is "'''lyonlog'''" and the password is "'''sxdtLy@log24'''". if you want to change the user or password before importing the SQL file, modify the query of line 27 after opening the download file by using an editor such as notepad. For example, a new query might be the below. | If you import the SQL file, it will create a user account, databases, and tables. The default user is "'''lyonlog'''" and the password is "'''sxdtLy@log24'''". if you want to change the user or password before importing the SQL file, modify the query of line 27 after opening the download file by using an editor such as notepad. For example, a new query might be the below. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
[[File:imradlog_sql.png|600px]] | [[File:imradlog_sql.png|600px]] | ||
| − | To import the SQL file, enter the <code>mysql</code> command. the <user> and < | + | To import the SQL file, enter the <code>mysql</code> command. the <user> and <password> is the existing account of the database in the dedicated log server. ''Note that if the operating system of your server is the Microsoft Windows, you must run the Command Prompt as administrator.'' |
| − | ''Note that if the operating system of your server is the Windows | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# mysql -u<user> -p<password> < <your_directory>/imradlog.sql | # mysql -u<user> -p<password> < <your_directory>/imradlog.sql | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
# mysql -uroot -pmypaddword < /home/user/imradlog.sql # linux | # mysql -uroot -pmypaddword < /home/user/imradlog.sql # linux | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==== Configuring Connection properties ==== | ||
| + | The next step is the configuration to have a daemon(i.e. the [[ImRAD services(daemons) | logexp]]) connect to the dedicated log server. | ||
| + | Open the "Dedicated Log server" page that is located in the "Environment" menu of the management interface and switch on the "Log Server". And then, you can see several forms to configure the connection properties. For more about the items, please refer to the [[Environment#Dedicated_Log_Server | Environment > Dedicated_Log_Server]] section. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The logexp service automatically reads the connection properties and copies local logs to your log server. If the "Last SQL Datetime" or the "Last Connection Datetime" is not updated in the "Dedicated Log server" page for several minutes, you need to [[CLI_-_Services(daemons)#Start.2C_Stop.2C_and_Restart | restart the logexp service]]. | |
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:41, 12 May 2021
Dedicated Log Server
You can operate a dedicated Log Server that can store more logs than the imRAD local database. If you configure it, the management interface reads logs from the dedicated Log Server and displays them.
| Log Table | Local Database | Log Server | Log name |
|---|---|---|---|
| IP/MAC address history | 3 months | 48 months | DHCP Lease |
| RADIUS Accounting | 3 months | 48 months | RADIUS Accounting |
| RADIUS post-auth | 3 months | 48 months | RADIUS Postauth |
Installing database server
Install MariaDB 10.0 or higher Database server on your server. MySQL 5.7 or higher is also available. It doesn't matter which operating systems of the database server.
Downloading an SQL file
Open the "Dedicated Log server" page that is located in the "Environment" menu of the management interface. And then, download an SQL file by clicking the icon on the top right of the "Target log" table and save it on your computer.
Importing an SQL file
Copy the SQL file into your log server(i.e. Dedicated Log server) and import it into your database by using the mysql command.
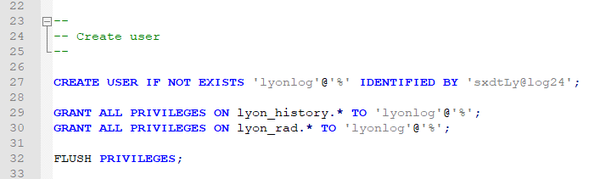
If you import the SQL file, it will create a user account, databases, and tables. The default user is "lyonlog" and the password is "sxdtLy@log24". if you want to change the user or password before importing the SQL file, modify the query of line 27 after opening the download file by using an editor such as notepad. For example, a new query might be the below.
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'myuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
The below picture is a part of the SQL.
To import the SQL file, enter the mysql command. the <user> and <password> is the existing account of the database in the dedicated log server. Note that if the operating system of your server is the Microsoft Windows, you must run the Command Prompt as administrator.
# mysql -u<user> -p<password> < <your_directory>/imradlog.sql # mysql -uroot -pmypaddword < c:\imradlog.sql # Windows # mysql -uroot -pmypaddword < /home/user/imradlog.sql # linux
Configuring Connection properties
The next step is the configuration to have a daemon(i.e. the logexp) connect to the dedicated log server. Open the "Dedicated Log server" page that is located in the "Environment" menu of the management interface and switch on the "Log Server". And then, you can see several forms to configure the connection properties. For more about the items, please refer to the Environment > Dedicated_Log_Server section.
The logexp service automatically reads the connection properties and copies local logs to your log server. If the "Last SQL Datetime" or the "Last Connection Datetime" is not updated in the "Dedicated Log server" page for several minutes, you need to restart the logexp service.